What is diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common vascular disease of the retina. It is caused by damage to the retinal blood vessels due to diabetic metabolic decompensation.
It can result in significant loss of vision.
What causes it?
When blood sugar levels are high, the walls of the retinal blood vessels are weakened and become more permeable, allowing fluid to enter the extracellular space. In more advanced cases, a proliferation of abnormal blood vessels are produced, causing bleeding.
The presence of blood in the vitreous space (the clear gel that fills the eyeball), causes it to become opaque, resulting in reduced vision that usually occurs abruptly.
How can it be prevented?
Sufferers of diabetes should have their blood glucose, blood pressure and plasma lipids closely monitored.
Other factors that can lead to diabetic retinopathy include obesity, smoking and physical inactivity.
Patients (totalling over 200 million worldwide) require regular retina check-ups as diabetic retinopathy does not generally produce symptoms until the damage is severe.
Symptoms
The patient is often unaware of the disease until severe damage has been caused. The symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Blurred vision and gradual loss of vision
- The appearance of spots or floaters
- Shadows or areas where vision is missing
- Difficulty seeing at night
Associated treatments
Retinopathy can affect the macula (the central area of the retina, responsible for detailed vision) or its periphery.
Depending on the area affected and the degree of development of the disease, specialists have different treatment options at their disposal, such as laser photocoagulation, intravitreal injections or surgery (vitrectomy).
Other visual complications associated with diabetes, such as glaucoma or cataracts, require specific treatments.
Specialists who treat this pathology
FAQs
Angiography is a technique used to delineate retinal or choroidal cases. Different contrasts are used, usually sodium fluorescein or indocyanine green. The scan is also useful for the diagnosis of other retinal diseases, such as pigment epithelium. In general, angiography is used to study many retinal diseases and their diagnosis.
Indocyanine green angiography is a technique used in some cases of AMD and serves to define the neovessels and, occasionally, to diagnose other diseases. Fluorescein angiography is the standard technique for studying blood vessel diseases and the retina in general.
It is a diagnostic technique to determine pathological and abnormal structures in the blood vessels and the different layers of the retina. It can be used in cases of macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, vasculopathy and many other macular disorders.
It is not counterproductive for any eye treatment.
Yes, after any eye operation, although it is advisable to wait several days for the scars to heal. It normally takes ten to twelve days to return to a normal life. It is always best to consult the doctor to find out about the risk factors.
In general, the patient can lead a normal life, unless there is gas inside the eye, in which case the patient should heed the advice of his doctor. Flying above 600–800 m and travelling over high mountain passes, either by train or car, should be avoided. If such needs arise, the ophthalmologist should be consulted.
It is much more likely for haemorrhages to occur after surgery, especially if a vitrectomy has been performed, in the case of patients with diabetic retinopathy. This is due to the vessel walls being extremely fragile in these patients and more prone to bleeding.
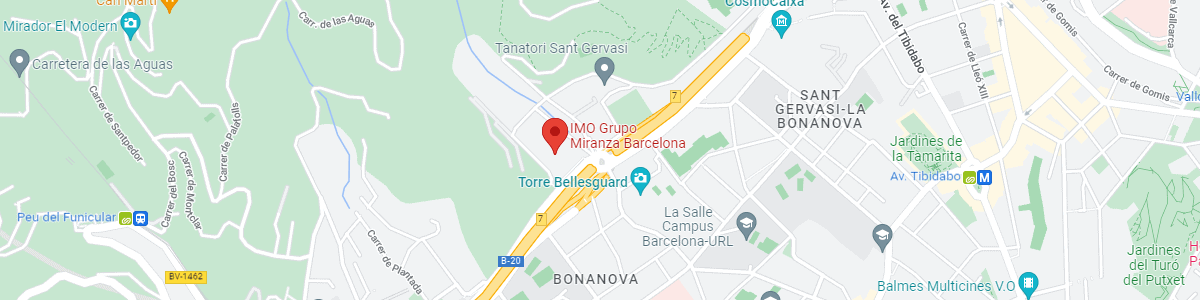
IMO Institute of Ocular Microsurgery
Josep María Lladó, 3
08035 Barcelona
Phone: (+34) 934 000 700
E-mail: international@imo.es
See map on Google Maps
By car
GPS navigator coordinates:
41º 24’ 38” N – 02º 07’ 29” E
Exit 7 of the Ronda de Dalt (mountain side). The clinic has a car park with more than 200 parking spaces.
By bus
Autobus H2: Rotonda de Bellesguard, parada 1540
Autobus 196: Josep Maria Lladó-Bellesguard, parada 3191
Autobuses H2, 123, 196: Ronda de Dalt – Bellesguard, parada 0071
How to arrive at IMO from:
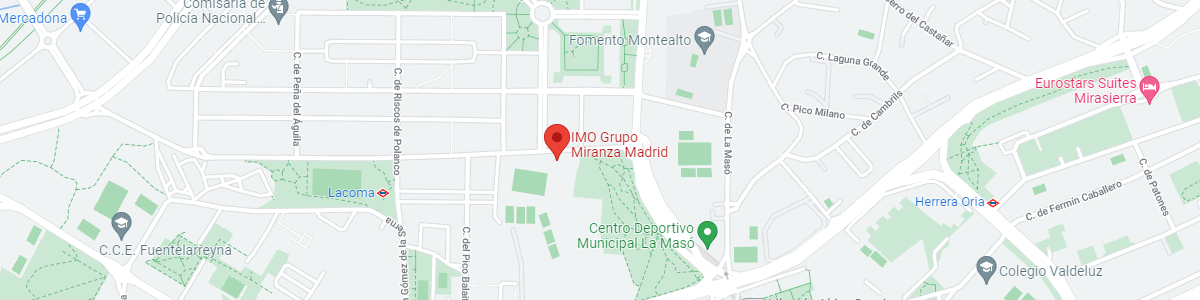
IMO Madrid
C/ Valle de Pinares Llanos, 3
28035 Madrid
Phone: (+34) 910 783 783
See map in Google Maps
Public transport
Metro Lacoma (líne 7)
Autobuses:
- Lines 49 & 64, stop “Senda del Infante”
- Line N21, stop “Metro Lacoma”
Timetables
Patient care:
Monday to Friday, 8 a.m. to 8 p.m.
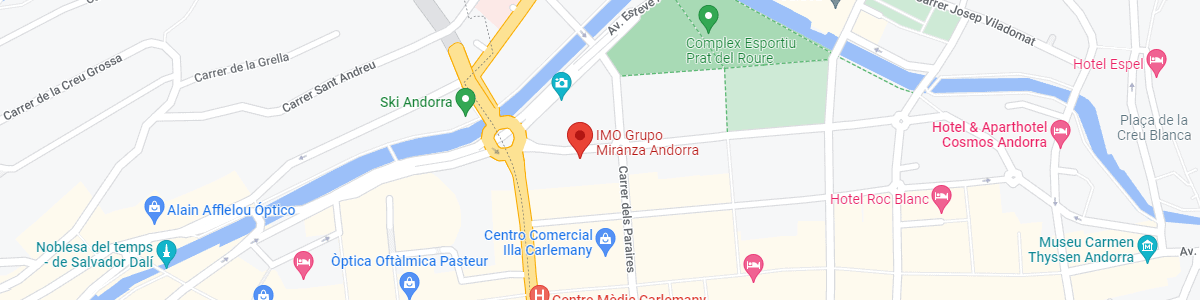
IMO Andorra
Av. de les Nacions Unides, 17
AD700 Escaldes-Engordany, Andorra
Phone: (+376) 688 55 44
See map in Google Maps
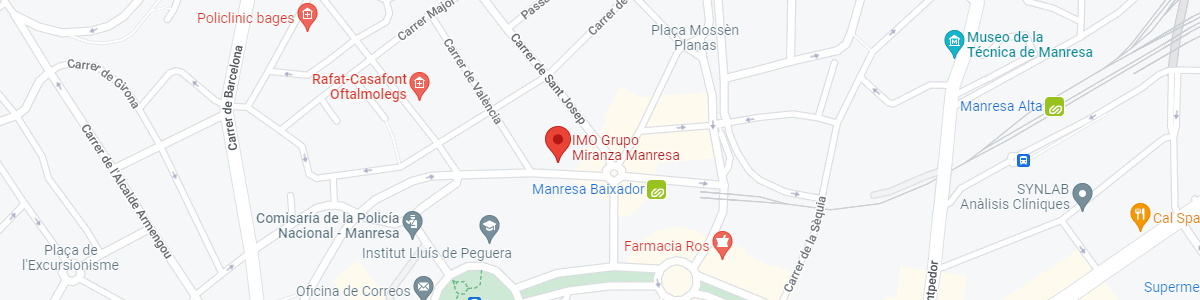
IMO Manresa
C/ Carrasco i Formiguera, 33 (Baixos)
08242 – Manresa
Tel: (+34) 938 749 160
See map in Google Maps
Public transport
FGC. Line R5 & R50 direction Manresa. Station/Stop: Baixador de Manresa
Timetables
Monday to Friday, 08:30 A.M – 13:30 PM / 15:00 PM – 20:00 PM