What is microperimetry?
Microperimetry is a diagnostic technique that measures the sensitivity of the macula and allows us to perceive any changes or incipient lesions in this central area of the retina, whose diameter is only 5 mm. It is therefore a very precise test, with which small scotomas or “blind spots” can be detected, which, by means of a conventional visual field (perimetry/campimetry), go unnoticed.
On the other hand, it also studies the patient’s fixation, that is, the location and stability of the preferred point of view.
What does it consist of?
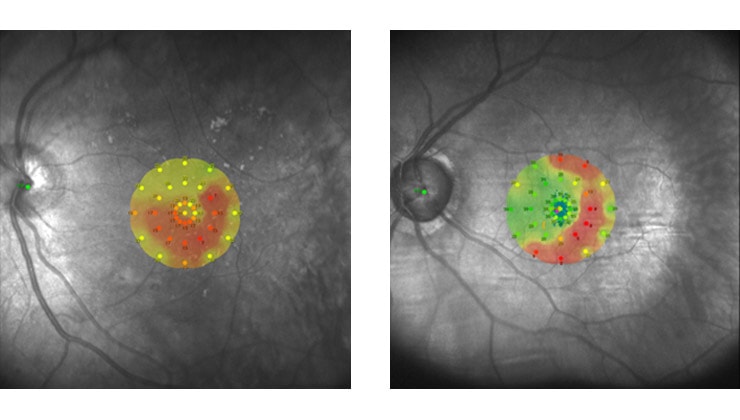
The computerized microperimeter projects light stimuli on different points of the retina to obtain a detailed “map” of the macular sensitivity to light and, simultaneously, perform a fixation analysis at each moment of the examination. These measurements are combined with real-time fundus imaging using SLO (Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy) technology to view the anatomy of the macula in great detail.
Thanks to a sophisticated eye-tracker system, this technology makes it possible to accurately correlate structural damage with its functional impact on the patient’s vision.
How is it performed?
This test does not require any preparation or dilation of the pupil and is performed in consultation by evaluating both eyes independently – first, covering one and then the other –, with a total duration of about 25 minutes.
To carry out microperimetry requires the active collaboration of the patient, who must press a button each time they perceive a light stimulus in different positions on the screen.
In what cases is it used?
Microperimetry, which was incorporated into IMO consultations in 2016, is especially indicated for the early diagnosis and monitoring of pathologies affecting the macula and, therefore, detailed vision and reading ability, among other precision activities. This is the case of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), hereditary retinal dystrophies – such as Stargardt disease, macular hole and macular oedema due to diabetic retinopathy or different pathologies.
Moreover, it is a very interesting tool for visual rehabilitation of low vision patients, as it incorporates specific software to train eccentric fixation and leverage the visual rest of patients in whom the centre of vision is affected. Thus, it is possible to stimulate a new preferred point of view and create a “false macula”.
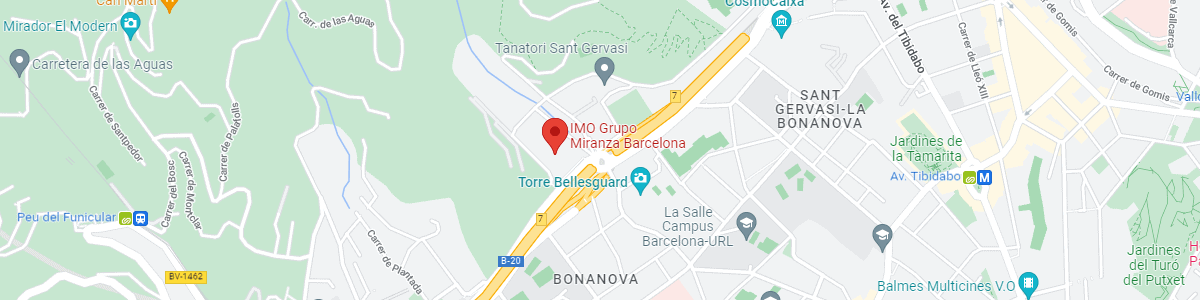
IMO Institute of Ocular Microsurgery
Josep María Lladó, 3
08035 Barcelona
Phone: (+34) 934 000 700
E-mail: international@imo.es
See map on Google Maps
By car
GPS navigator coordinates:
41º 24’ 38” N – 02º 07’ 29” E
Exit 7 of the Ronda de Dalt (mountain side). The clinic has a car park with more than 200 parking spaces.
By bus
Autobus H2: Rotonda de Bellesguard, parada 1540
Autobus 196: Josep Maria Lladó-Bellesguard, parada 3191
Autobuses H2, 123, 196: Ronda de Dalt – Bellesguard, parada 0071
How to arrive at IMO from:
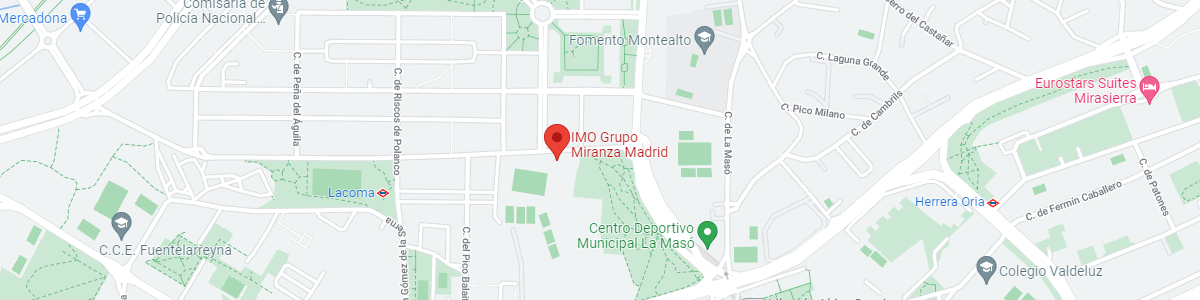
IMO Madrid
C/ Valle de Pinares Llanos, 3
28035 Madrid
Phone: (+34) 910 783 783
See map in Google Maps
Public transport
Metro Lacoma (líne 7)
Autobuses:
- Lines 49 & 64, stop “Senda del Infante”
- Line N21, stop “Metro Lacoma”
Timetables
Patient care:
Monday to Friday, 8 a.m. to 8 p.m.
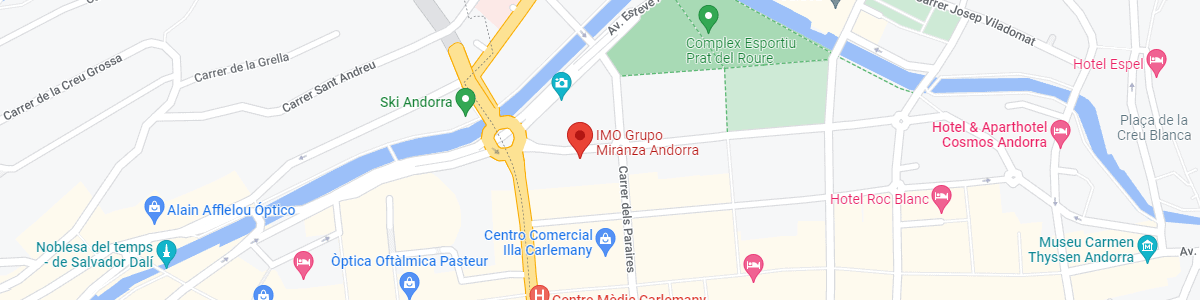
IMO Andorra
Av. de les Nacions Unides, 17
AD700 Escaldes-Engordany, Andorra
Phone: (+376) 688 55 44
See map in Google Maps
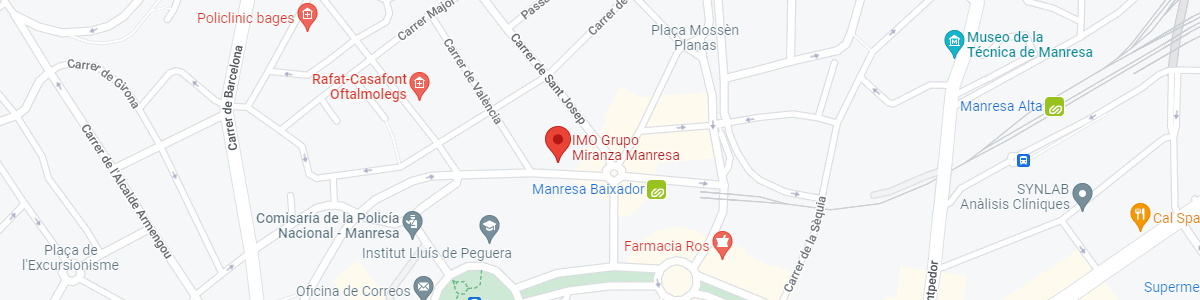
IMO Manresa
C/ Carrasco i Formiguera, 33 (Baixos)
08242 – Manresa
Tel: (+34) 938 749 160
See map in Google Maps
Public transport
FGC. Line R5 & R50 direction Manresa. Station/Stop: Baixador de Manresa
Timetables
Monday to Friday, 08:30 A.M – 13:30 PM / 15:00 PM – 20:00 PM